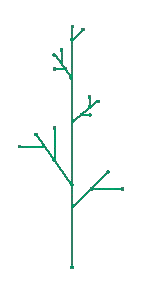
 Recent applications
Recent applications
A tree is any graph in which a path can be found between any vertex and any other without using a ‘circular’ route. If each edge is labelled with a number (or weight) representing cost or distance, then a problem arises in finding the shortest path between two vertices (which minimizes cost or distance). This problem was solved by Dijkstra in 1959. Applications include the design of transport networks, and cluster analysis in statistics.
Oriented or directed graphs assign a direction to each edge, and are used in analysis of social systems (sociograms, family trees, kinship diagrams ... ) and critical path analysis (flow diagrams) for job scheduling.
 Recent applications
Recent applications